April 11, 1954, is the most boring day ever, according to a Cambridge computer scientist who used a search engine with a database with over 300 million facts. Don’t be judgmental, we know a couple of cool things happened, but there was no Google to check it. Well, a couple of decades have passed and life is anything but boring right now.
Bright Side wants to show you 15 people whose ordinary day turned into an absolutely wild adventure after a surprising discovery.
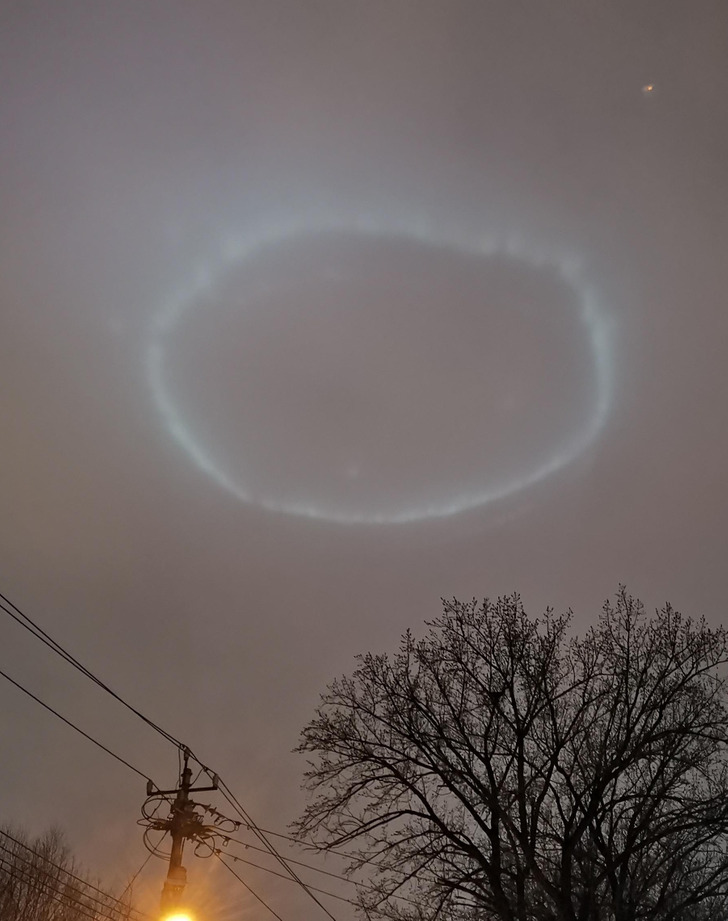
1. “This circle that appeared in the evening sky”

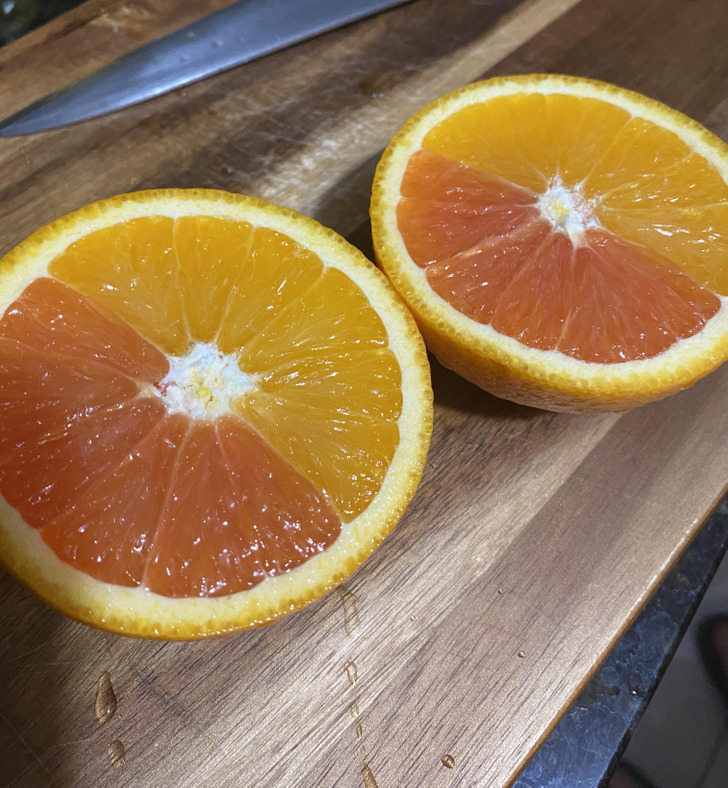
2. “My orange has 2 sides.”

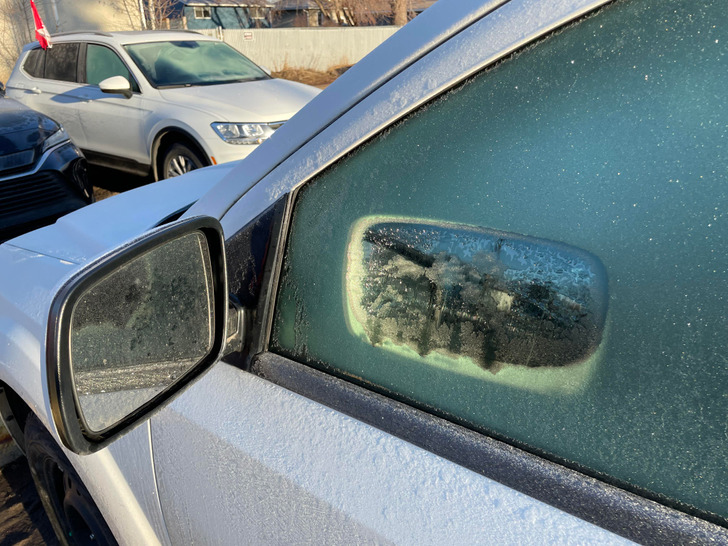
3. “The sun reflecting off my side mirror melted a mirror-shaped hole in the frost on the window.”

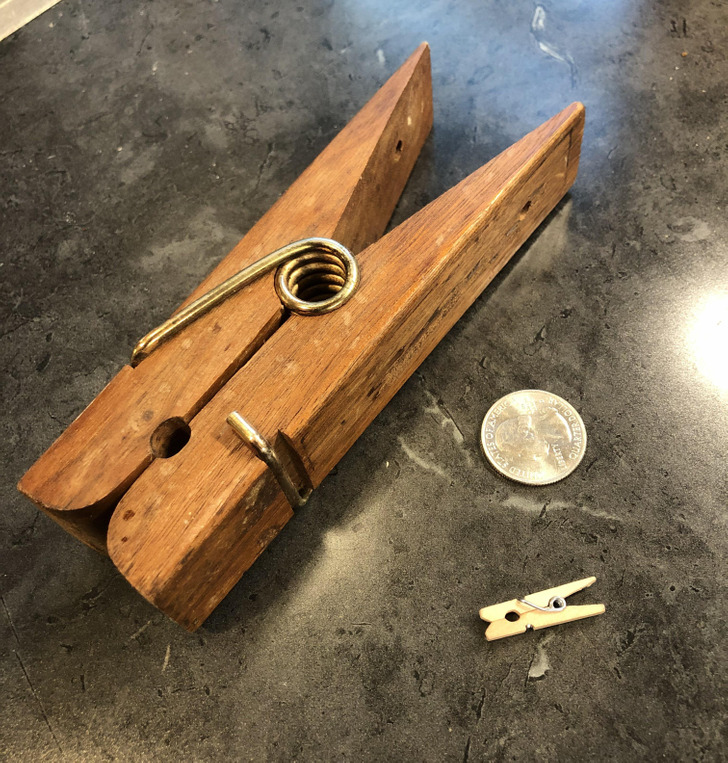
4. “I have a ridiculously oversized clothespin I found years ago and now I’ve found its ridiculously micro-sized little brother.”

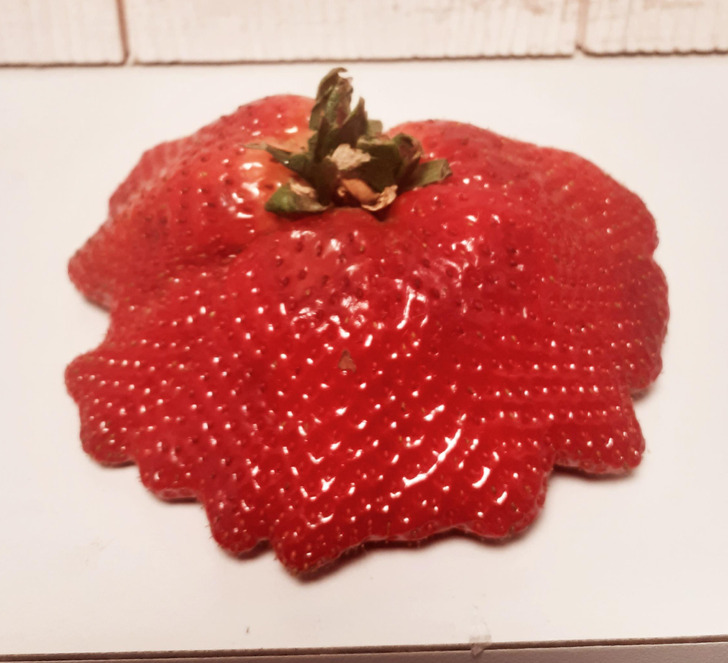
5. “Saw this mega strawberry.”

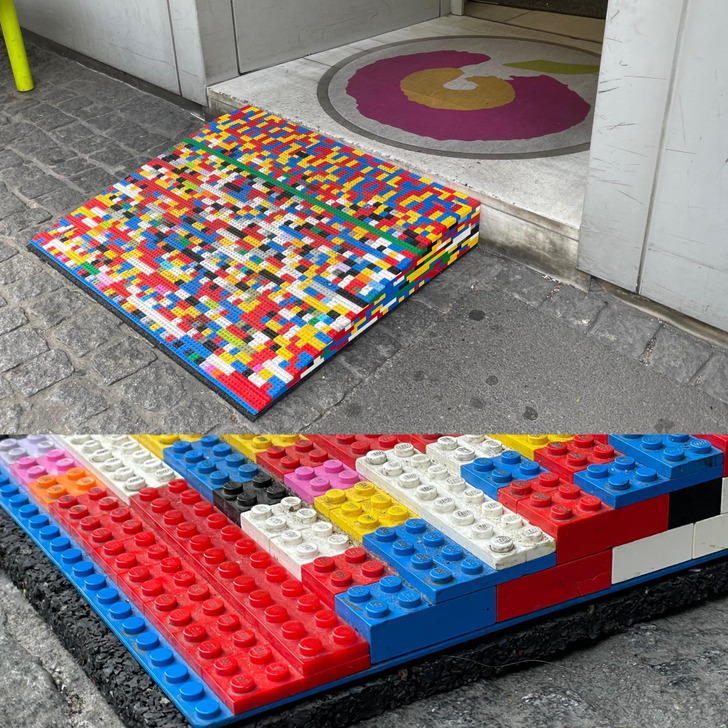
6. “This wheelchair ramp is made out of Legos.”

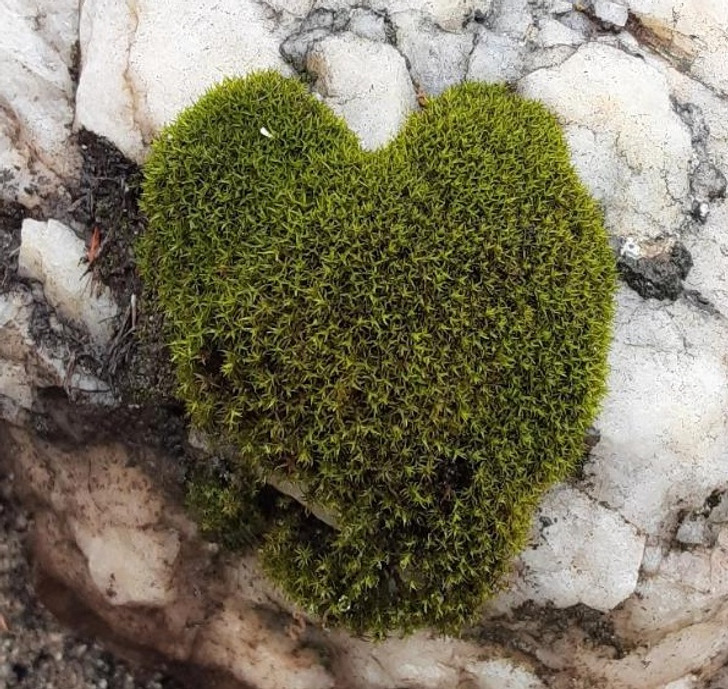
7. “This moss in the shape of a heart”

8. “Caught a yellow garden spider eating a lady bug at the perfect moment.”
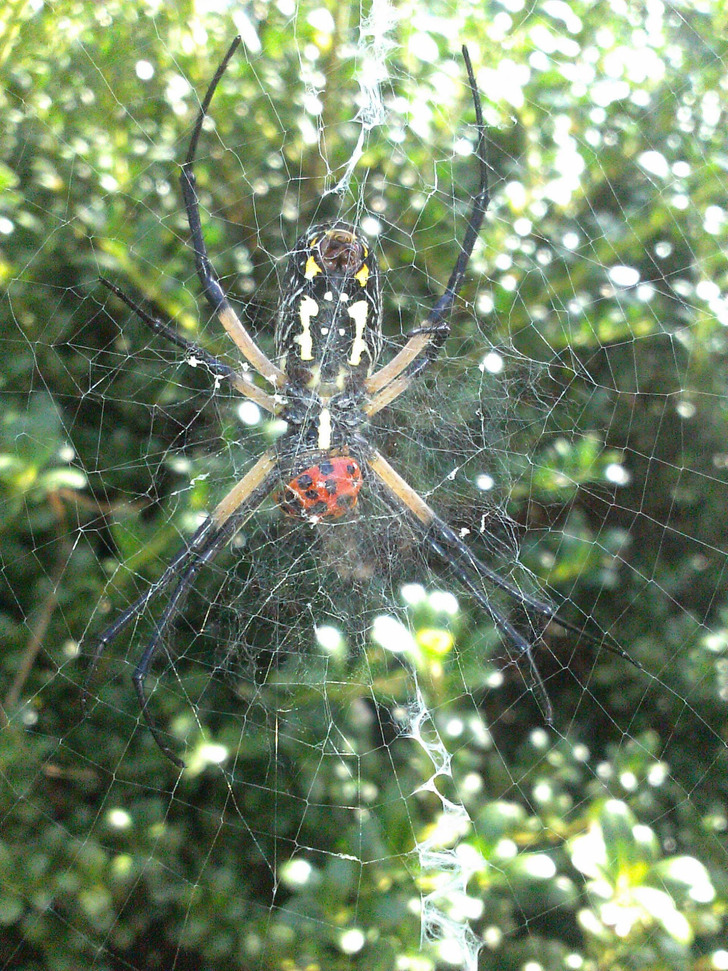

8. “Caught a yellow garden spider eating a lady bug at the perfect moment.”

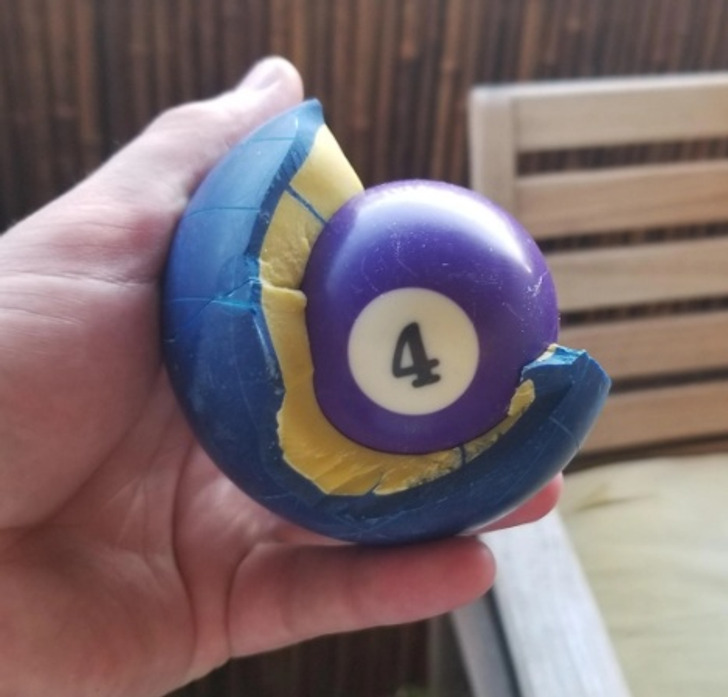
10. “There was a billiard ball inside of my bocce ball.”

11. “It was a great day till this moment.”

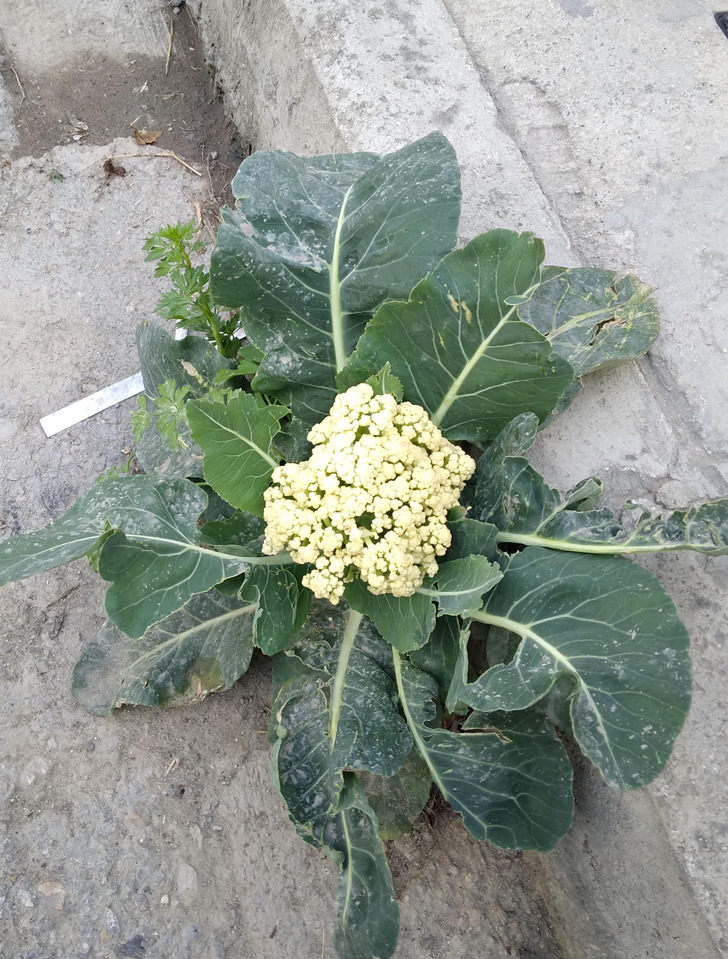
12. “Found a cauliflower growing straight out of a concrete curb in my street.”

13. “Found a tiny, seemingly ripe, orange.”

14. “My friend’s bruise resembles The Mona Lisa.”
15. “Found a rock in the shape of a skull on a Scottish Mountain.”

What was the most unusual thing you saw this week? Drop a comment.
Preview photo credit TheAcademy_ / Reddit
A woman is getting a lot of praise for refusing to give up her first-class plane seat for a child.
It wasn’t her problem that they couldn’t plan ahead.
A woman who decided not to give up her first-class seat on a flight, even though she was traveling with a toddler, has gotten a lot of support on social media for her choice.
Dr. Sabra, who goes by @lifewithdrsabra on TikTok, shared her experience in a recent video.
She was asked to change her seat, 1A, to help another passenger.
In her video, Dr. Sabra added some text on the screen that said:

“From my point of view: The flight attendant asks me if I want to give up my seat 1A so a child can sit with their family.”
She had a big smile while sharing this message, showing she was happy to keep the seat she had paid for.
She even added a popular TikTok audio in the background where someone says, “Girl, forget those kids and forget you too.”
This clip is often used in videos where people refuse to give up something for someone else’s children.
The 1A seat, usually found in first class at the front of the plane, is a very desirable spot for travelers.
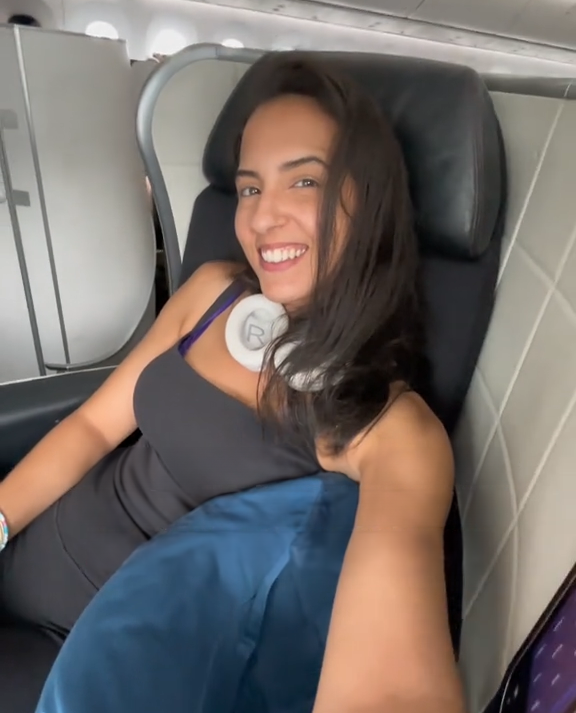

Dr. Sabra shared more details in the caption of her video.
She said she chose to keep her seat and that the family was able to “find a solution” to their seating problem without her having to move.
In her caption, she wrote: “That’s a no from me, would you have given up your seat?
“Plus, they found a solution, so I’m not a terrible person. Also, the child was about 13.”
The video has gone viral, getting 4.9 million views, and many viewers are supporting her choice in the comments.



Leave a Reply