Pregnancy is a life-changing journey, not just physically but mentally. While many focus on the visible bodily transformations, few realize the incredible changes happening inside the brain. New research reveals that pregnancy rewires the brain in ways that enhance bonding, emotional intelligence, and responsiveness to a baby’s needs. So, is “baby brain” a real thing? The answer may surprise you—it’s not about forgetfulness but about fine-tuning the mind for motherhood.
The Science Behind Pregnancy Brain Changes

If you’ve ever heard a pregnant woman joke about “baby brain,” you might assume it means forgetfulness or mental fog. However, neuroscientists have discovered that the brain undergoes structural remodeling, improving areas linked to nurturing and caregiving.
Dr. Emily Jacobs, a neuroscientist from the University of California, Santa Barbara, explains that pregnancy doesn’t damage the brain but optimizes it for motherhood. “Think of it like a sculptor refining a masterpiece,” she says. “It’s not about losing cognitive function but gaining specialized skills to care for a baby.”
These changes start as early as nine weeks into pregnancy and continue beyond birth, shaping how a mother interacts with and responds to her child.
How Pregnancy Rewires the Brain
Neuroscientists have studied the brains of pregnant women using MRI scans and found some surprising patterns:
Video : Your Brain Changes All the Time, but Being a Mom Changes It Forever
✔ Reduction in Gray Matter – Out of 400 brain regions studied, 80% showed a decline in gray matter, particularly in areas responsible for processing emotions and social interactions. This might sound concerning, but it actually helps the brain become more efficient at understanding emotions.
✔ Increased Activity in Emotional Centers – The amygdala, which regulates emotions, becomes more active, making mothers more sensitive to their baby’s facial expressions, cries, and needs.
✔ Stronger Neural Connections – White matter, the brain’s communication network, becomes more efficient, allowing different regions to work together more effectively. This boosts a mother’s ability to multitask and respond quickly to her child.
✔ Enhanced Social Cognition – Mothers experience heightened social awareness, helping them recognize potential threats and improve bonding with their baby.
Is “Baby Brain” a Myth?
Many women report feeling forgetful during pregnancy, but studies suggest that memory loss is not the defining feature of pregnancy brain. Instead, the brain reorganizes itself to focus on what truly matters:
🔹 Understanding social cues
🔹 Enhancing emotional intelligence
🔹 Developing stronger attachment responses
🔹 Improving problem-solving skills related to caregiving
Rather than becoming scattered or absent-minded, pregnant women prioritize information differently. Everyday distractions may take a backseat, but when it comes to responding to their baby, mothers show increased cognitive efficiency.
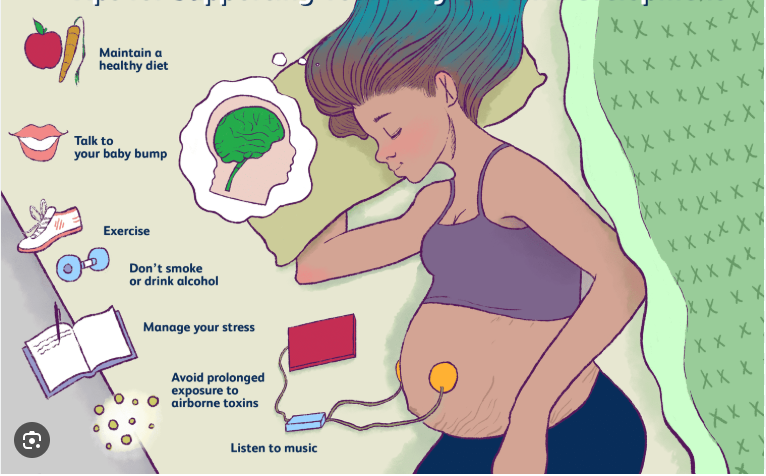
Pregnancy Creates a “Window of Learning”
Scientists believe that pregnancy opens a unique learning window, allowing women to quickly adapt to the challenges of motherhood.
Dr. Ronald Dahl, a neuroscientist at the University of California, Berkeley, explains that pregnancy hormones reshape priorities and motivations, making women more focused on caregiving and more skilled at recognizing their baby’s needs.
This heightened awareness isn’t limited to just birth—it extends well into the postpartum period, helping mothers develop expertise in infant care without formal training.
Brain Changes Last Beyond Birth
While some pregnancy-related changes fade over time, others persist for years.
✔ Gray matter reduction remains for up to two years postpartum, ensuring mothers stay highly attuned to their child’s emotional needs.
✔ Brain scans can accurately identify whether a woman has been pregnant, proving that the structural changes are long-lasting.
✔ Some cognitive enhancements remain for life, helping mothers stay emotionally responsive and socially aware even after their children grow up.
Not Just Biological Mothers Experience These Changes

While pregnancy hormones drive these changes, they aren’t exclusive to biological mothers. Research shows that fathers, adoptive parents, and primary caregivers who engage in hands-on childcare also exhibit brain changes, particularly in areas related to empathy and emotional processing.
According to Dr. Jonny Kohl, a researcher in parenting and neurobiology, the brain starts preparing for parenthood long before birth. While pregnancy hormones accelerate the process, caregiving itself can reshape the brain in profound ways, reinforcing the idea that parenting is a learned skill, not just a biological instinct.
How These Changes Impact Motherhood
The neurological transformation of pregnancy offers many benefits that go beyond just bonding with a baby. These changes help new mothers:
✔ Handle stress more effectively – The brain strengthens its emotional resilience, helping moms stay patient even during sleepless nights.
✔ Recognize subtle emotional cues – Mothers become more attuned to facial expressions, cries, and body language, allowing them to respond instinctively to their baby’s needs.
✔ Develop stronger multitasking abilities – White matter improvements make it easier to juggle multiple responsibilities without feeling overwhelmed.
✔ Build deeper connections – Increased emotional intelligence helps mothers form stronger relationships, not just with their babies but also with family and friends.
Video : New Study Says Pregnancy Changes the Brain
The Emotional Side of Pregnancy Brain
These brain changes can also make new moms more emotionally sensitive, which may contribute to postpartum mood swings. Understanding that these shifts are part of a natural neurological process can help new mothers navigate postpartum challenges with confidence.
Dr. Jacobs emphasizes that the brain is wired to prioritize caregiving. So, if you ever feel more emotional after childbirth, remember—it’s not a weakness. It’s proof that your brain is adapting to motherhood.
Conclusion: Pregnancy Brain Is a Superpower, Not a Flaw
Forget the myth that pregnancy makes women forgetful or mentally slower. Science now proves that pregnancy fine-tunes the brain for motherhood, enhancing emotional intelligence, social awareness, and problem-solving skills.
From strengthening caregiving instincts to boosting multitasking abilities, pregnancy permanently reshapes the brain to ensure mothers are prepared for the challenges of parenthood.
So, the next time someone jokes about “baby brain,” you can confidently reply:
“Actually, my brain just got an upgrade.”
A Woman Demands Bigger Airline Seats for Her Butt, Looks Unrecognizable in Old Photos
A young model has sparked a global conversation with a simple request: make airplane seats wider. The influencer pleads that bodies are changing and hence, airplane seats should be made bigger too. When faced with criticism, the model revealed she has not had any surgeries to enhance her butt and shared old photos.
A viral dilemma.
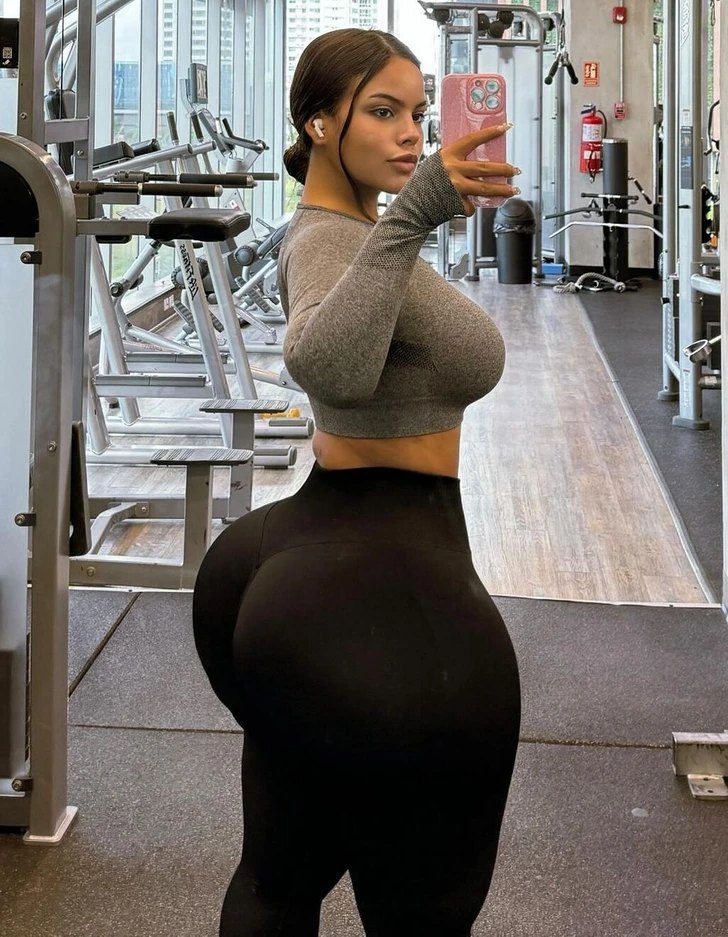

Gracie Bon, a social media star from Panama, went viral when she shared a video of herself on a plane. It showed her struggling to buckle up in an airplane seat. Her discomfort was evident as she tried to adjust herself in the cramped space. The video struck a chord with many, spreading like wildfire across social media platforms.
She elaborated on her struggle and many resonated with her.
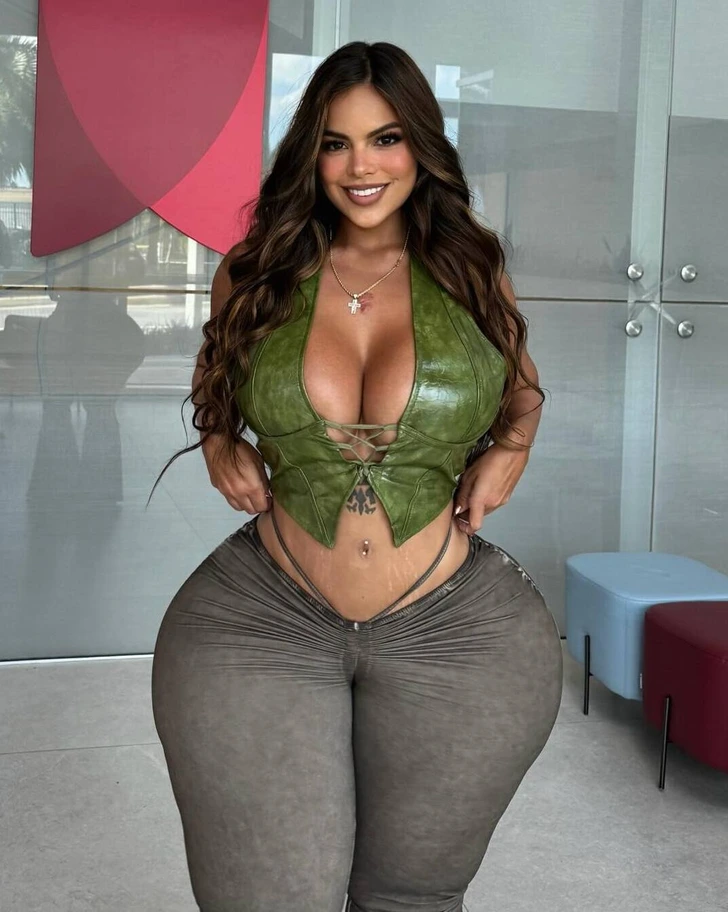

Despite booking first-class tickets, Gracie found no respite. She faced the same issue. The seats were still just too small for her curvaceous figure.
This led her to voice a bold statement. She urged airplanes should have bigger seats. She also argued that it’s not her responsibility to change her body to fit into the seats.
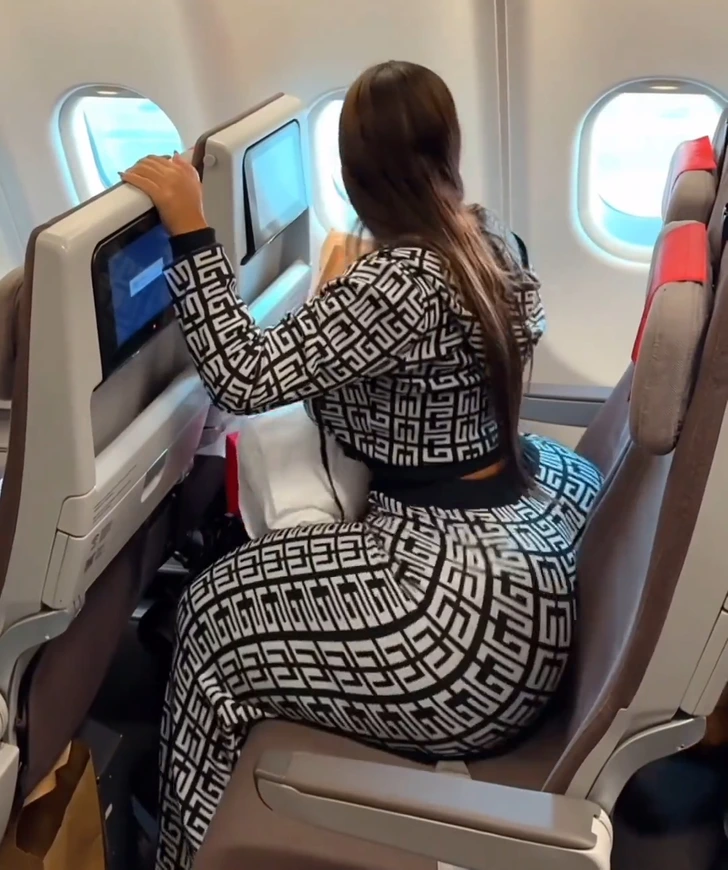

Gracie’s message received both support and criticism.
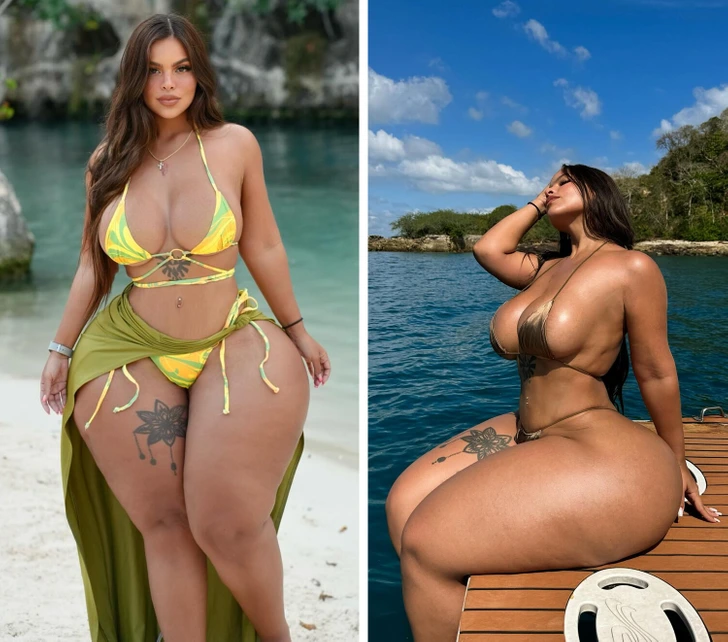

Gracie’s outspokenness brought mixed reactions. While some applauded her for standing up for plus-sized individuals, others criticized her. They suggested that her body’s proportions were a result of plastic surgery. Gracie stood firm, countering that her physique was natural. She requested that the airline industry adapt to accommodate everyone despite their size.
The model shared her impressive transformation journey.
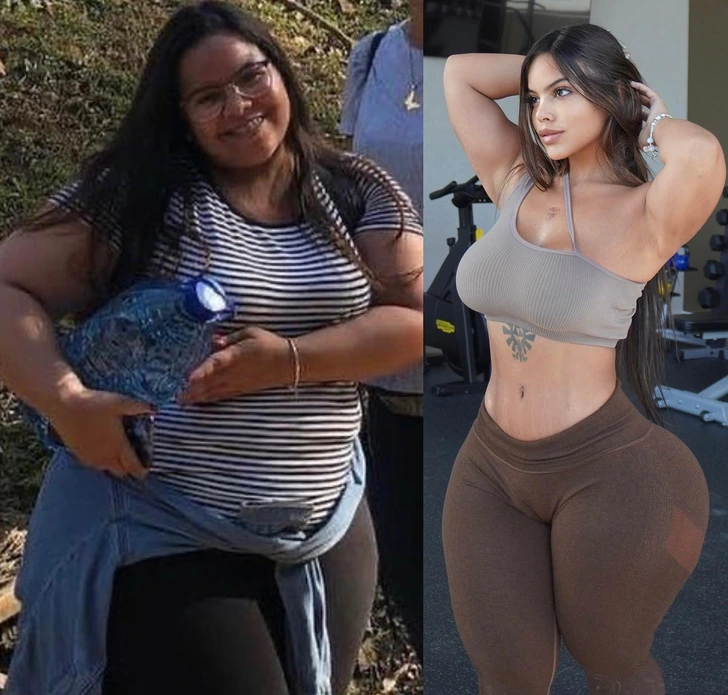

Putting the negative comments about her having surgery to make her butt bigger to rest, Gracie spoke out. She shared before and after photos of herself. She clarified that she used to weigh 300 lbs (136 kg).
When she was 21 years old, she decided to adopt a healthier lifestyle. She started working out and taking care of herself. She also added that she made such a decision as her weight started affecting her health and led to knee pain and breathing issues.
She admitted to having surgeries on her upper body.
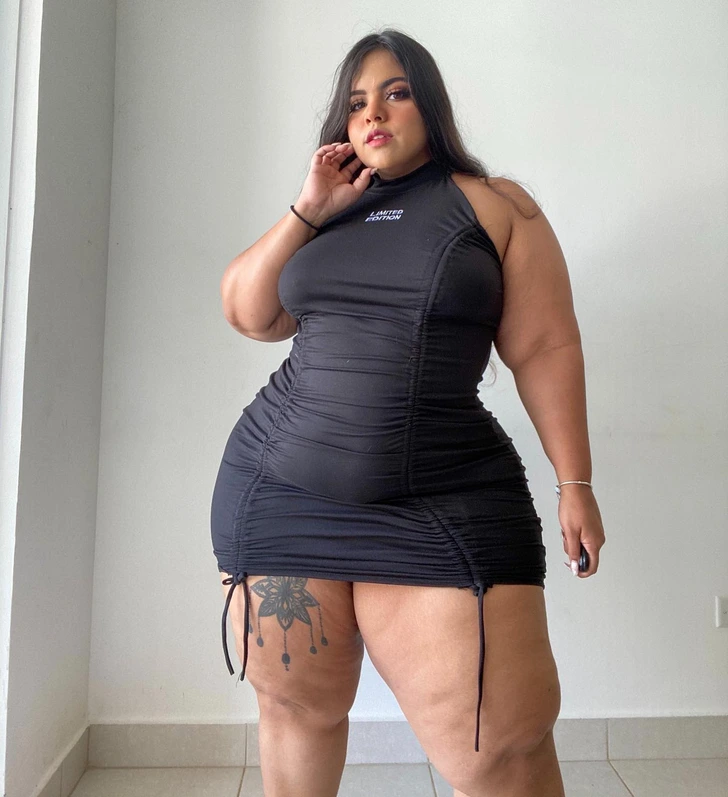

Gracie successfully lost 100 lbs (45 kg). She confesses that to deal with extra skin, she opted for surgery. In fact, she says she had «many» small surgeries to remove the loose skin. Gracie also promotes body positivity and believes that no one body type is superior. We should all feel comfortable in our own skin without giving into beauty standards.
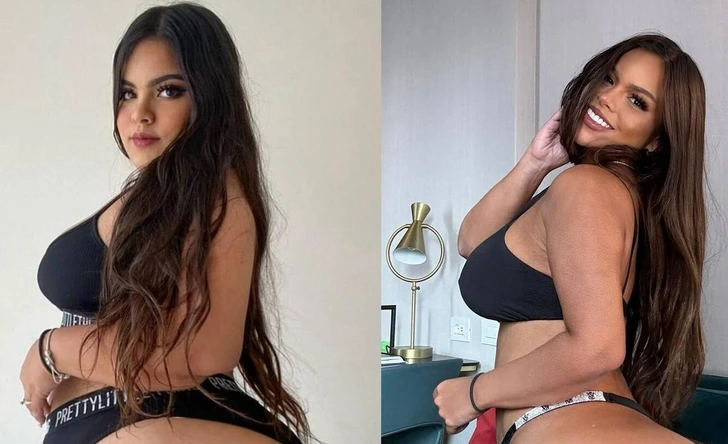

Many people still had various questions. Some asked how she was able to only lose weight in her upper body. Others questioned how her face changed completely. A few also wondered if she edits her photos. Gracie is yet to comment on these concerns.
Another woman made headlines for her surprising transformation. She removed all of her teeth. You can read about it here.
Preview photo credit graciebon / Instagram, graciebon / Instagram, graciebon / Instagram



Leave a Reply