It is a reminder that even in the darkest of times, there is always the potential for kindness and compassion.
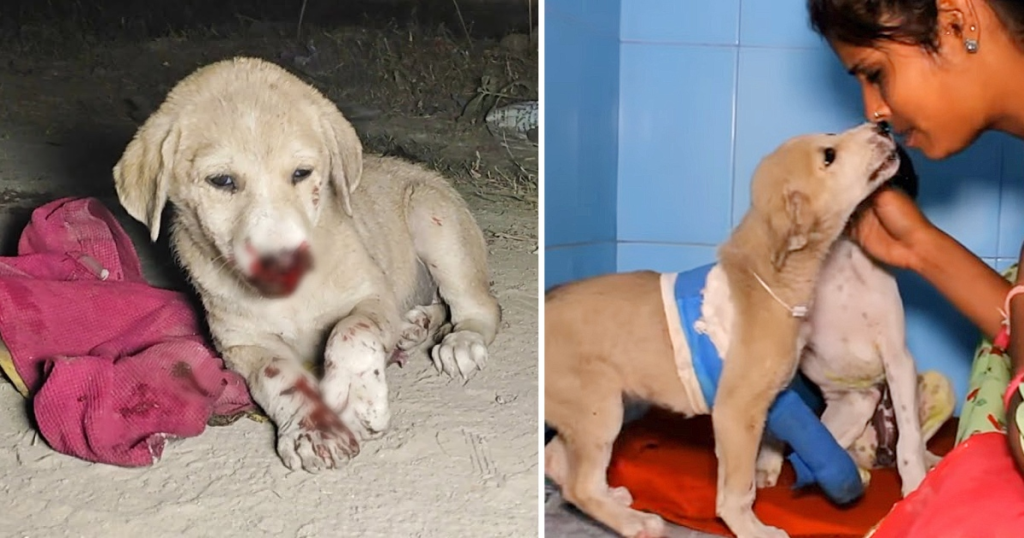
This brave little girl was saved by a nice passer-by after her nose bled heavily, splattering her legs with clotted blood. She was put onto a carry-basket and evaluated for injuries, including a seriously sprained leg.

Despite her suffering and bewilderment, she proved to be a tough braveheart. After getting pain treatment, supporting bandages, and many of love, her tail produced a little wag, indicating her life-loving enthusiasm.
This story of courage and resilience is an uplifting reminder of the strength of the human spirit. It is a monument to the power of kindness and compassion, and how even the tiniest acts of kindness can make a difference in someone’s life.

The little girl’s story is a reminder of the necessity of being prepared for medical crises. It is crucial to have a first aid kit on available and to know how to utilize it. It is also important to know how to spot the signals of a medical emergency and to ask for aid if required.

It is also important to be aware of the risks associated with specific activity. For example, if a child is playing outside, it is important to make sure they are wearing protective clothing and that they are monitored. It is also important to be aware of the potential for injuries and to take actions to prevent them.

Lastly, it is important to remember that even in the most terrible of situations, there is always hope. This little girl’s story is a reminder that even in the face of misfortune, there is always the potential for resilience and courage.

It is a reminder that even at the worst of circumstances, there is still the potential for kindness and compassion.
Amazing Rescue: Mother Dog and Puppies Discover Paradise on Lush Green Meadows, Escaping the Scorching Desert Sun!
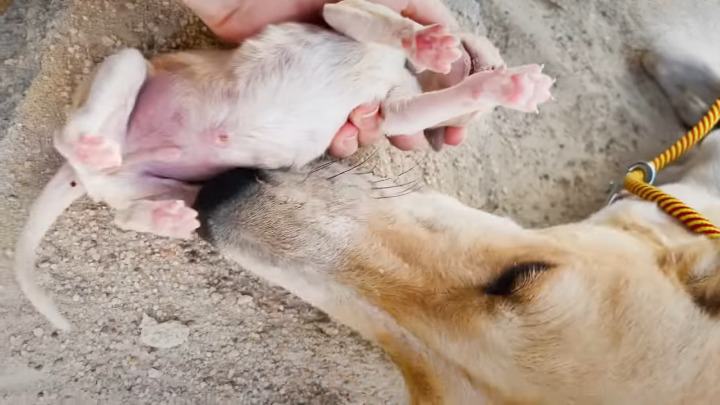

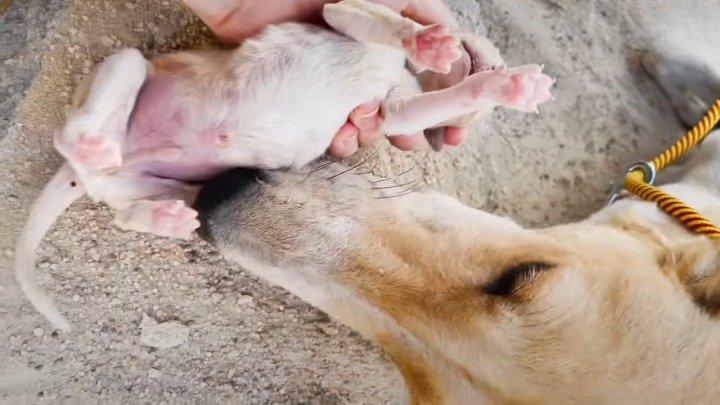
When it comes to motherhood, animals can be just as nurturing and protective as humans. This was proven by a mama dog found in the middle of a 122-degree desert with her puppies. Fortunately, their heartwarming story has a happy ending.

The mama dog and her puppies were discovered by a group of hikers who were trekking through the desert. The puppies were huddled close to their mother, trying to find some shade and relief from the scorching heat.
Upon seeing the desperate situation of the family, the hikers called the local animal rescue team. The rescue team immediately responded and arrived at the scene to rescue the mama dog and her puppies.
The rescue team found the family in poor health, severely dehydrated, and malnourished. They immediately provided them with water and food to revive their strength. After assessing their condition, the rescue team transported them to a veterinary clinic for further examination and treatment.
It was at the veterinary clinic that the mama dog and her puppies experienced a simple yet life-changing moment – they saw grass for the first time! It was an emotional and heartwarming sight as the puppies started to frolic in the green grass, while the mama dog watched over them with a happy and contented look on her face.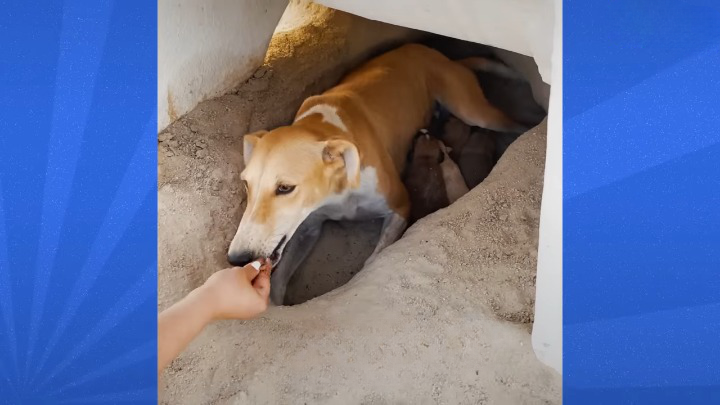
The mama dog’s maternal instincts shone through, as she watched her puppies enjoy their newfound freedom and joy. The moment was a reminder that even the simplest things can bring joy and happiness to those in need.
After several days of treatment and rehabilitation, the mama dog and her puppies were given a clean bill of health. They were then transferred to a local animal shelter, where they would be available for adoption
.
This incredible story of a mama dog and her puppies rescued from scorching desert heat is a reminder of the power of kindness and compassion. The hikers who discovered them and the rescue team who saved their lives demonstrated the true spirit of humanity. The mama dog’s love for her puppies and their joy in experiencing the simple pleasures of life are an inspiration to us all.
In conclusion, the story of the mama dog and her puppies found in the middle of a 122-degree desert is a testament to the resilience of animals and the compassion of humans. It’s a story of survival, hope, and the importance of kindness. The joyful reaction of the puppies to green grass for the first time is a reminder that even in the most difficult circumstances, happiness can be found in the simplest things.



Leave a Reply